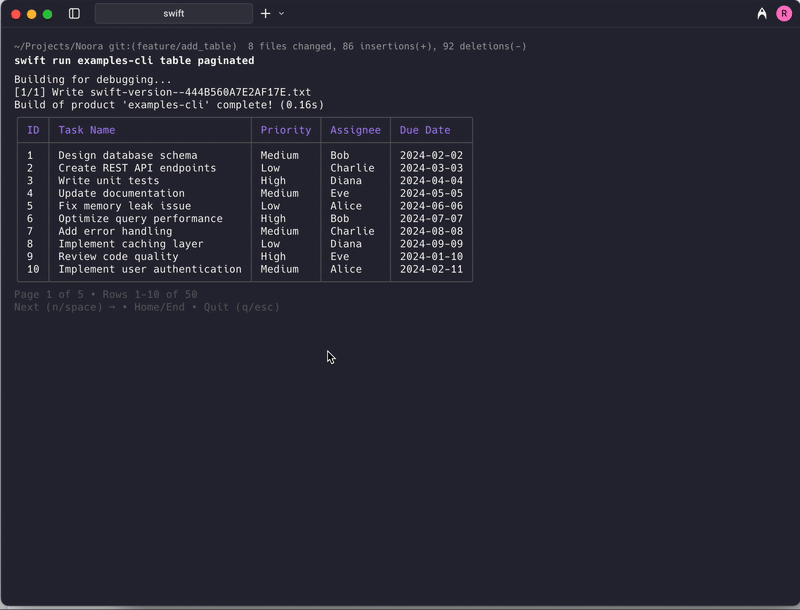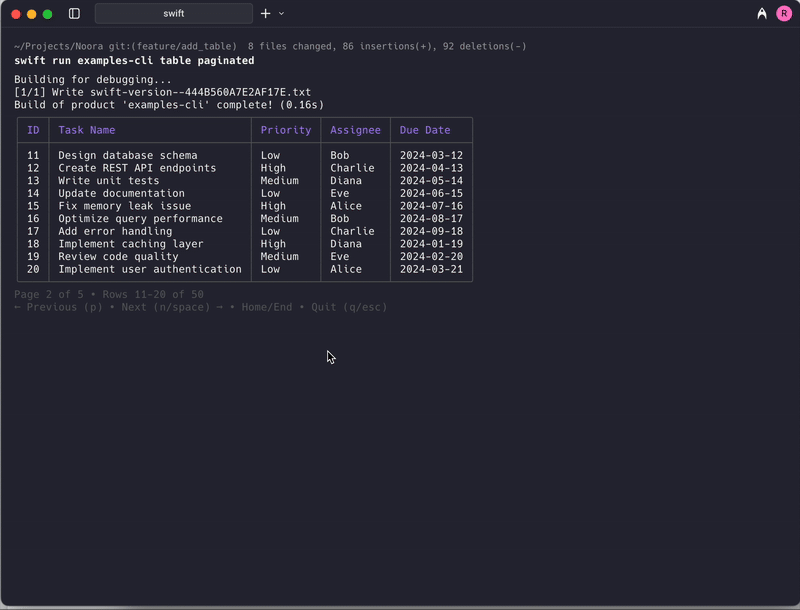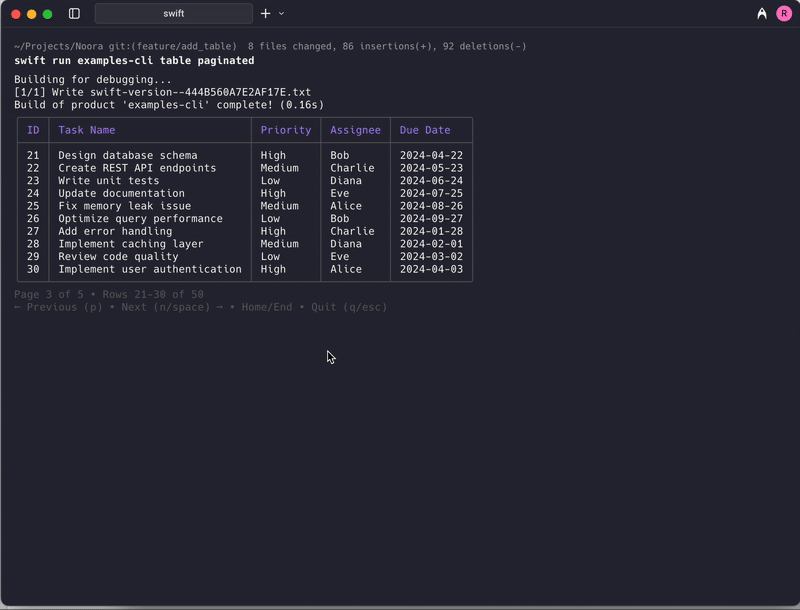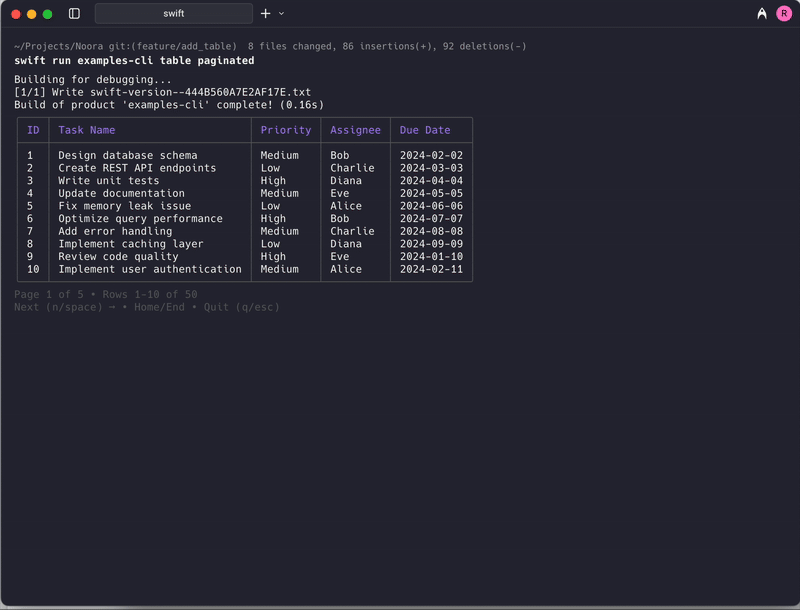
Paginated Table
This component displays large datasets in a paginated format, allowing users to navigate through multiple pages of data. It's perfect for displaying extensive lists, logs, or any dataset that would be overwhelming to show all at once. Users can navigate between pages using keyboard controls without selecting individual rows.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactivity | Optional (falls back to displaying data without pagination) |
Demo
API
Basic Example
// Simple paginated table with string arrays
let noora = Noora()
// Large dataset that will be split across multiple pages
let largeDataset = [
["React", "18.2.0", "Active"],
["Vue", "3.3.4", "Active"],
["Angular", "16.1.0", "Deprecated"],
["Svelte", "4.0.5", "Active"],
["Ember", "5.1.0", "Maintenance"],
["Alpine.js", "3.12.0", "Active"],
["Preact", "10.15.1", "Active"],
["Solid", "1.7.8", "Active"],
["Qwik", "1.2.6", "Active"],
["Lit", "2.7.5", "Active"]
]
try noora.paginatedTable(
headers: ["Framework", "Version", "Status"],
rows: largeDataset,
pageSize: 4
)Advanced Example with TableData
// Advanced paginated table with custom styling and column configuration
let columns = [
TableColumn(title: "Package", width: .flexible(min: 15, max: 25), alignment: .left),
TableColumn(title: "Version", width: .fixed(12), alignment: .center),
TableColumn(title: "Downloads/Month", width: .fixed(15), alignment: .right),
TableColumn(title: "Status", width: .auto, alignment: .right)
]
let rows: [[TerminalText]] = [
[
TerminalText("React"),
TerminalText("\(.primary("18.2.0"))"),
TerminalText("\(.accent("20.1M"))"),
TerminalText("\(.success("Active"))")
],
[
TerminalText("Vue"),
TerminalText("\(.primary("3.3.4"))"),
TerminalText("\(.accent("4.1M"))"),
TerminalText("\(.success("Active"))")
],
[
TerminalText("Angular"),
TerminalText("\(.muted("16.1.0"))"),
TerminalText("\(.muted("2.8M"))"),
TerminalText("\(.warning("Deprecated"))")
],
[
TerminalText("Svelte"),
TerminalText("\(.primary("4.0.5"))"),
TerminalText("\(.accent("400K"))"),
TerminalText("\(.success("Active"))")
],
[
TerminalText("Ember"),
TerminalText("\(.secondary("5.1.0"))"),
TerminalText("\(.muted("150K"))"),
TerminalText("\(.warning("Maintenance"))")
],
[
TerminalText("Alpine.js"),
TerminalText("\(.primary("3.12.0"))"),
TerminalText("\(.accent("250K"))"),
TerminalText("\(.success("Active"))")
]
]
let tableData = TableData(columns: columns, rows: rows)
try noora.paginatedTable(tableData, pageSize: 3)Semantic Styling Example
// Paginated table with semantic styling for better visual hierarchy
let headers: [TableCellStyle] = [
.primary("Framework"),
.secondary("Version"),
.accent("Popularity"),
.accent("Status")
]
let frameworks: [StyledTableRow] = [
[.plain("React"), .success("18.2.0"), .success("Very High"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Vue"), .success("3.3.4"), .success("High"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Angular"), .muted("16.1.0"), .secondary("Medium"), .warning("Deprecated")],
[.plain("Svelte"), .success("4.0.5"), .secondary("Growing"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Ember"), .secondary("5.1.0"), .muted("Low"), .warning("Maintenance")],
[.plain("Alpine.js"), .success("3.12.0"), .secondary("Medium"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Preact"), .success("10.15.1"), .secondary("Medium"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Solid"), .success("1.7.8"), .secondary("Growing"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Qwik"), .success("1.2.6"), .secondary("New"), .success("Active")],
[.plain("Lit"), .success("2.7.5"), .secondary("Medium"), .success("Active")]
]
try noora.paginatedTable(
headers: headers,
rows: frameworks,
pageSize: 5
)Lazy Loading Example
For large datasets that come from an API or database, you can load pages on demand instead of loading all data upfront:
// Lazy loading paginated table - pages are fetched on demand
let noora = Noora()
try await noora.paginatedTable(
headers: ["ID", "User", "Email", "Status"],
pageSize: 20,
totalPages: 50, // Known upfront (e.g., from API metadata)
startPage: 0, // Optional: start at a specific page
loadPage: { page in
// Fetch data for the requested page
let response = try await api.fetchUsers(page: page, perPage: 20)
return response.users.map { [$0.id, $0.name, $0.email, $0.status] }
}
)The lazy loading mode:
- Shows a loading indicator while fetching each page
- Caches loaded pages - navigating back won't re-fetch
- Displays error messages if a page fails to load
- Allows retry (press
r) when an error occurs
Error Handling
do {
try noora.paginatedTable(
headers: ["ID", "Name", "Description"],
rows: generateLargeDataset(), // Your data generation function
pageSize: 10
)
print("User finished browsing the paginated data")
} catch {
print("Paginated table failed: \(error)")
// This might happen in non-interactive terminals
}Options
Basic paginated table method
| Attribute | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
headers | Array of column header strings | Yes | |
rows | Array of row data (each row is an array of strings) | Yes | |
pageSize | Number of rows per page | Yes | |
renderer | A rendering interface that holds the UI state | No | Renderer() |
Advanced paginated table method with TableData
| Attribute | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
data | TableData object with custom columns and content | Yes | |
pageSize | Number of rows per page | Yes | |
renderer | A rendering interface that holds the UI state | No | Renderer() |
Semantic styling method
| Attribute | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
headers | Array of column headers with semantic styling | Yes | |
rows | Array of row data with semantic styling | Yes | |
pageSize | Number of rows per page | Yes | |
renderer | A rendering interface that holds the UI state | No | Renderer() |
Lazy loading method (async)
| Attribute | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
headers | Array of column header strings | Yes | |
pageSize | Number of rows per page | Yes | |
totalPages | Total number of pages (known upfront) | Yes | |
startPage | Initial page to display (0-indexed) | No | 0 |
loadPage | Async callback (Int) async throws -> [[String]] to fetch a page | Yes |
Navigation Controls
The paginated table supports the following keyboard controls:
| Key | Action |
|---|---|
→ / n / Space | Go to next page |
← / p | Go to previous page |
Home / g | Go to first page |
End / G | Go to last page |
r | Retry loading (when error occurs) |
q / Esc | Exit pagination view |
Page Information Display
The component automatically displays pagination information:
- Current page number and total pages
- Page navigation hints at the bottom
- Row range display (e.g., "Showing 1-10 of 50 entries")
- Navigation instructions for keyboard controls
Use Cases
The paginated table is ideal for:
- Log file viewing: Browse through large log files page by page
- Database records: Display query results in manageable chunks
- File listings: Show directory contents with many files
- Configuration data: Present extensive configuration options
- API responses: Display paginated API results
- Reports: Show large reports in digestible sections
Behavior
Unlike the interactive table:
- No row selection: Users browse data without selecting specific rows
- Navigation only: Focus is on moving between pages and viewing data
- Read-only interaction: Users can only view and navigate, not select
- Automatic pagination: Data is automatically split based on
pageSize
Non-Interactive Terminals
When running in a non-interactive terminal (e.g., CI/CD pipelines):
- Static mode: Displays all data at once without pagination
- Lazy loading mode: Loads and displays only the initial page
Error Conditions
The paginated table may throw errors in the following situations:
- Page load failure (lazy loading): When the
loadPagecallback throws an error - Invalid page size: When
pageSizeis less than 1
Performance Considerations
- Memory efficient: Only renders the current page, not the entire dataset
- Lazy loading: For very large datasets, use the async API to load pages on demand
- Page caching: Loaded pages are cached, so navigating back is instant
- Fast navigation: Page switching is immediate for cached pages
- Responsive: Adapts to terminal size changes automatically
